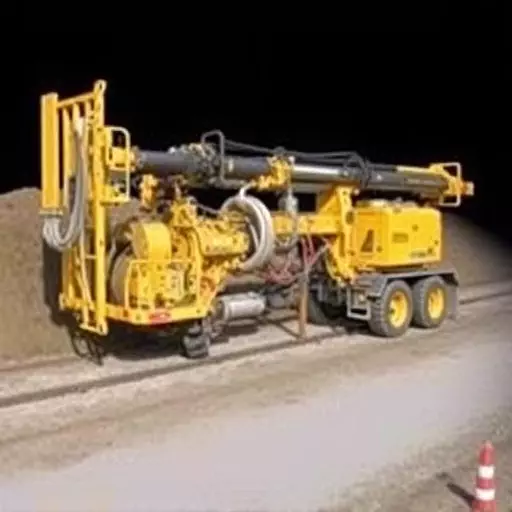
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) is a cutting-edge trenchless technology that enables precise installation of large-diameter pipelines beneath urban areas, rivers, and roads with minimal surface disruption. By using hydraulic pressure and steering mechanisms, HDD avoids traditional excavation, reducing environmental impact, community disturbances, and damage to existing infrastructure. This versatile method, including Directional Boring Toledo, is preferred for new installations and rehabilitation projects due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ability to navigate challenging terrains. Best practices in HDD projects involve strategic decision-making based on site assessments, effective mud management, regular equipment maintenance, and adherence to operational protocols. Although initial costs are higher, technological advancements continue to make HDD a promising game-changer for future infrastructure development, including utility installation and underwater projects.
“Unleashing the potential of Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) revolutionizes pipeline installation, particularly for large-diameter projects. This advanced trenchless technology offers a seamless solution, replacing traditional excavation methods. The article delves into the transformative power of Directional Boring Toledo, exploring its advantages and technical nuances. From efficient route planning to minimizing environmental impact, HDD emerges as a game-changer in infrastructure development. We dissect its benefits, challenges, and future prospects, highlighting why it’s an indispensable tool for large-scale projects.”
- Understanding Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) and Its Advantages for Large-Diameter Pipelines
- The Role of Directional Boring in Trenchless Technology: A Case for Efficient Pipeline Installation
- Technical Considerations and Best Practices for HDD Projects Using Large-Diameter Pipelines
- Benefits, Challenges, and Future Prospects of HDD for Constructing and Maintaining Large-Scale Infrastructure
Understanding Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) and Its Advantages for Large-Diameter Pipelines
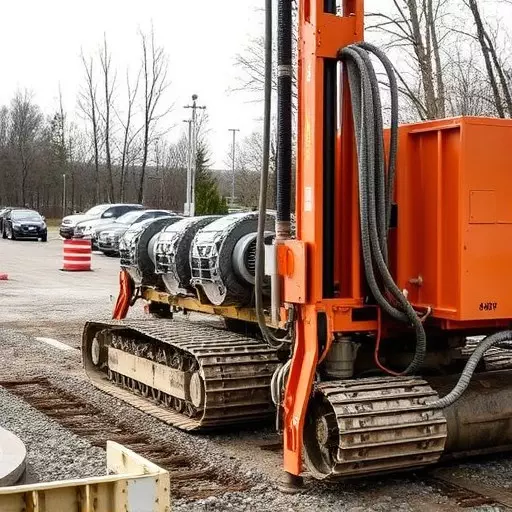

Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) is a specialized technique used for installing large-diameter pipelines beneath existing surfaces, such as roads, rivers, and urban areas. This method involves directing a drill bit along a predetermined path using hydraulic pressure and steering mechanisms. Unlike traditional excavation methods, HDD minimizes surface disturbance, making it ideal for trenchless technology applications.
The advantages of HDD for large-diameter pipelines are significant. It allows for the installation of pipelines with minimal environmental impact, reducing the need for massive excavation projects that can disrupt communities and cause extensive damage to infrastructure. Furthermore, HDD offers greater accuracy in directing pipes precisely, ensuring optimal alignment and minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding utilities and structures. This technology has revolutionized pipeline construction, making it a preferred method for both new installations and rehabilitation projects.
The Role of Directional Boring in Trenchless Technology: A Case for Efficient Pipeline Installation

Directional boring, facilitated by Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD), is a revolutionary technique within Trenchless Technology that’s transforming pipeline installation. This method allows for the precise excavation and routing of pipes through the ground, minimizing the need for traditional trenching methods. By employing HDD Toledo, contractors can install large-diameter pipelines with enhanced efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and lower overall costs.
The benefits of HDD extend beyond cost savings and ecological considerations. It enables the installation of pipelines in challenging terrain, including areas with limited access, high water tables, or sensitive ecosystems. Moreover, HDD’s ability to create continuous, curved tunnels ensures a more seamless integration of pipes into existing landscapes, reducing surface disruptions and minimizing project delays.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices for HDD Projects Using Large-Diameter Pipelines

When undertaking Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) projects with large-diameter pipelines, careful technical considerations and best practices are essential to ensure successful and safe operations. The choice of equipment, including powerful drills and robust pipe jacking machines, is crucial for navigating through challenging soil conditions and accurately placing the pipeline. In-depth site assessment, considering factors like ground composition and water tables, guides strategic decision-making to mitigate potential issues.
Adhering to best practices involves implementing effective mud management systems to control dust and stabilize cuttings, enhancing safety and environmental protection. Regular maintenance of equipment and strict adherence to operational protocols are vital for preventing mechanical failures and ensuring project efficiency. Additionally, utilizing advanced Trenchless Technology allows for minimal disruption to surrounding infrastructure, making HDD a preferred method for large-diameter pipeline installations.
Benefits, Challenges, and Future Prospects of HDD for Constructing and Maintaining Large-Scale Infrastructure

The adoption of Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) for large-diameter pipelines has brought about significant advantages in the construction and maintenance of substantial infrastructure projects. One of the key benefits is its ability to minimise disruption to existing surfaces, making it an ideal solution for urban or environmentally sensitive areas. HDD allows for the installation of pipelines without the need for extensive excavation, thereby reducing project timelines and costs associated with traditional methods. This trenchless technology also exhibits enhanced safety as it minimises the risk to workers and local communities during construction.
Despite its advantages, there are challenges that must be addressed. The complex nature of HDD projects requires specialised equipment and skilled operators, which can increase initial investment and operational costs. Furthermore, navigating through diverse geological formations presents technical difficulties, demanding careful planning and adaptation. However, continuous advancements in technology, such as improved drilling fluids, advanced guidance systems, and enhanced machinery, are overcoming these challenges. Looking ahead, the future of HDD for large-scale infrastructure appears promising, with potential applications extending beyond pipelines to other areas like utility installation and underwater projects, thus further solidifying its role in the evolution of construction and maintenance methodologies.